Types | Causes | Symptoms | Diagnosis | Complications & Effects | Treatment | Surgery
What is Pediatric Flatfoot?
Pediatric flatfoot is a condition typical of children having fallen arches in the soles of their feet. When the kids stand straight barefoot, their soles completely touch the floor with no arches in the middle.
What are the Types of Flat Feet?
There are two major types of flat feet: flexible and rigid flat feet.
• Flexible Flatfoot:
Flexible flatfoot occurs if a kid’s foot arch sags while standing, reappearing when they sit or walk on their toes. Most children with this condition overcome it as they grow and exercise more. Simple exercises such as walking here and there can help tighten tendons in the feet, eventually shaping the sole’s arch.
Pain is rare in this condition, but when a child reports feeling pain, it is important to see a medical professional. In case of discomfort, help the child with stretching exercises and provide shoes with inserts to support their arches.
Children usually outgrow this condition as they grow older. However, flexible flatfeet may advance into rigid flatfeet if it is not corrected as the child grows. The condition may result due to inheritance, tightness of foot muscles or even wearing the wrong type of shoes.
• Rigid Flatfoot:
This is a permanent condition where the joints in the foot become immobile due to the fusion of bones in the foot. The arch in the foot is absent whether a child is in a sitting or standing position. Although most people are born with this condition, others develop it due to injury or infection.
It may also result due to the presence of extra cartilage in the arch area of the foot. Rigid flat feet can only be treated if identified at an early stage, probably at birth. The flat feet may be accompanied with pain in a focused, specific area of the foot.
What Causes Flat Feet in Children?

Some children are born with this condition. It is inheritable from one’s line of ancestry. Children who have Down’s syndrome are at a higher risk of developing this condition due to laxity. Disorders of movement such as cerebral palsy may also be a cause of flattened feet in children.
Other causes may include malformation of a bone, weak arches, rickets, dysfunction, muscle disease or fusion of tendons in the sole of the feet.
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Flat Feet?
Signs are what can be seen by a patient or someone else. A symptom is what is felt by an individual with regards to a condition or disease. Some extreme cases of flat feet may cause children’s legs and knees to rotate and face inwards. Most children do not have signs or symptoms of flat feet. However, some may experience the following:
- Pain in the feet while walking.
- Cramps in the feet.
- Tenderness of the sole.
- Change in walking position.
- Difficulty in using shoes.
- Stiffness of the feet.
- Children frequently wanting to be carried.
- Sagging of the arches.
- Muscle exhaustion after prolonged standing periods.
- Withdrawal from physical activities such as sports.
How are Flat Feet Diagnosed?
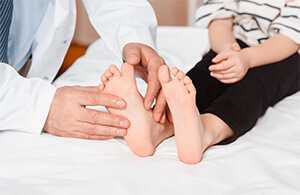
A medical professional should be consulted if a child’s feet flatten, get stiffer, becomes painful or their condition continues to deteriorate despite engaging in recommended flat feet exercises. A doctor in various positions can diagnose a child’s feet. The child can be asked to sit, walk or stand as the doctor examines their feet from all angles.
A doctor can also get children to stand on their toes for examination of the difference in the shape of their feet, including functionality. Podiatrists have the ability to differentiate between flexible and rigid flat feet. The severity of the sag on the arch under different positions such as sitting, walking or even standing can help diagnose flatfeet in children.
In flexible flatfeet, the condition is only present when a child is standing on their feet. However, the arch reappears when the child is asked to walk on their toes or sit. On the other hand, children with rigid flatfeet experience no change in their feet despite changing their postures.
X-rays may be done in cases where the condition is accompanied with pain to examine the severity of the condition. Once the diagnosis is done, the correct form of treatment is accorded to the child. Flat feet do not only cause pain in the arch but also in some other parts of the body.
What Are the Possible Complications & Effects?
Flat feet can cause children’s legs and knees to turn inwards, causing further complications. Other effects of this condition include:
- Problems in the knee due to bone misalignment.
- Pain and discomfort in the bones when active.
- Ankles with inflammation.
- Development of lifestyle diseases. Idleness due to pain arising when feet muscles are active lead to weight gain. Later, the condition can result in diseases such as obesity and cardiovascular diseases.
- Development of poor body posture.
- Reduced ability to exercise.
What are the Best Treatment Options?
1. Shoe Modifications:

People with flat feet should wear shoes made with modifications aimed at curving their arches. Such shoes support the arch by giving it a lift as you walk. The shoes are basically designed to do what a normal arch would do. Stability of the shoes is also an important consideration. People with flat feet tend to have legs that curve inwards.
The shoes hold children’s feet in place to correct the turning effect, in addition to controlling leg motions by aligning their legs in a straight line.
2. Maintain Normal Weight:
Children with obesity exert high pressure on their feet, causing flat feet. Normal weight should be maintained to minimize the pressure exerted when standing or walking for long durations. Regular exercises such as walking and eating healthy foods can help foster weight loss and maintenance of normal weight.
3. Activity Modifications:
Children should avoid walking or standing for long periods to reduce the pressure exerted on their feet. They need to rest their feet and protect them from disturbance. As a result, they protect their feet from further injury or complications. Activities that would cause discomfort or further harm to a child’s feet must be avoided.
4. Orthotic Devices:
Orthotic devices can help prevent pain and discomfort that might result from prolonged standing or walking. The devices are inserted in a child’s shoes to support their arches. Whereas functional orthotics devices are made using hard materials, accommodative orthotics devices are made from softer fabrics.
Despite the differences, they both provide enough support and cushion to children’s feet. The devices reduce pain. Use the right orthotics prescribed by an experienced professional to get the best results.
5. Physical Therapy:

Physical therapy is care given to help relieve pain from injuries and assist in movement. A physiotherapist can examine a child’s feet to determine the severity of the condition. Feet are responsible for supporting the body as its pillars, hence must be cared for and kept strong.
Physiotherapy can help reduce back, knee or ankle pain. It involves a therapist engaging a child’s feet in stretching exercises daily. Ice application is also done to minimize inflammation. The therapists also give children shoes designed to offer arch support modifications.
All these are done to correct walking postures. Therapists recommend surgery only in extreme cases if pain becomes unbearable.
6. Medications:
Children diagnosed with flat feet are treated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen. These drugs can help reduce pain and inflammation.
When is Surgery Needed?
Surgery is done based on the type of flat foot a child has or severity of the malformation. Although flexible flat feet often disappear as a child grows, kids with rigid flat feet may require surgery to realign tendons in their feet. If non-surgical methods fail to relieve a child from discomfort, it becomes necessary to opt for surgery as a treatment option.
Surgery becomes necessary if a child is in pain and thus needs relief. It may also be done to improve foot functionality in children with flat feet.
Flat feet surgery may be done to reposition the arch, lengthen the heel bone for enhanced foot support in case of extreme arch sag; tighten arch tendons to offer pain relief, or insert an implant in between affected bones to improve foot arch support.
Sources:
The Podiatry Institute, A Systematic Approach to Pediatric Flatfoot
Podiatry Today, When Pediatric Flatfoot Requires Surgical Correction
National Center for Biotechnology Information, Pediatric Flexible Flatfoot; Clinical Aspects and Algorithmic Approach